What is Swarm?
The complete vision of Swarm is described in detail in The Book of Swarm written by Swarm founder Viktor Tron, with further high level details described in the whitepaper. More in depth low level implementation details can be found in the Swarm Specification paper. The latest research and technical papers from Swarm can be found on the "Papers" section of the Ethswarm homepage.
Swarm is peer-to-peer network of nodes which work together to provide decentralised storage and communication infrastructure.
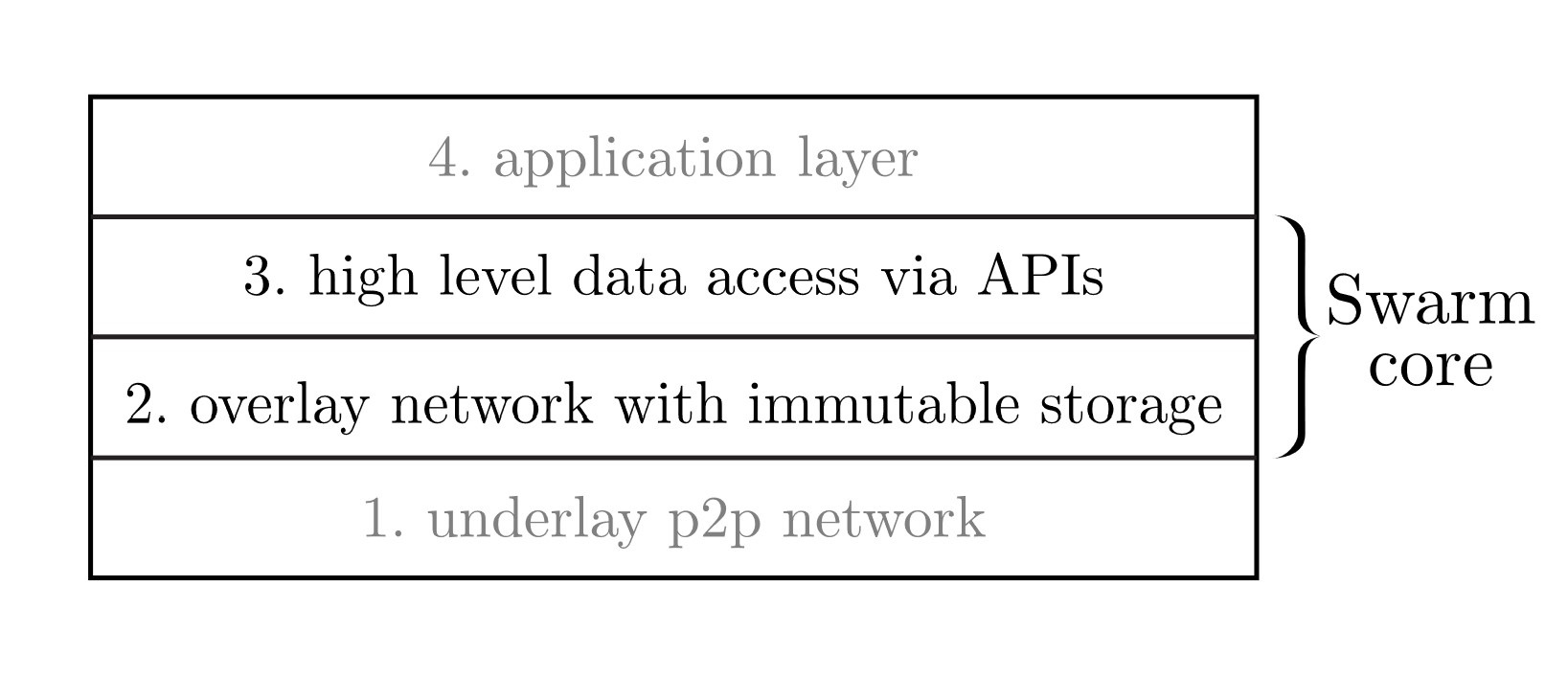
Swarm can be divided into four main parts:
- Underlay Network - A peer-to-peer network protocol to serve as underlay transport. Swarm's underlay network is built with libp2p.
- Overlay Network - An overlay network with protocols powering a distributed immutable storage of chunks (fixed size data blocks).
- Data Access Layer - A component providing high-level data access and defining APIs for base-layer features.
- Application Layer - An application layer defining standards and outlining best practices for more elaborate use cases.
Of these four main parts, parts 2 and 3 form the core of Swarm.
1. Underlay Network
The first part of Swarm is a peer-to-peer network protocol that serves as the underlay transport. The underlay transport layer is responsible for establishing connections between nodes in the network and routing data between them. It provides a low-level communication channel that enables nodes to communicate with each other directly, without relying on any centralised infrastructure.
Swarm is designed to be agnostic of the particular underlay transport used, as long as it satisfies certain requirements described in The Book of Swarm.
As the libp2p library meets all these requirements it has been used to build the Swarm underlay network.
2. Overlay Network
The second part of Swarm is an overlay network with protocols powering the Distributed Immutable Store of Chunks (DISC). This layer is responsible for storing and retrieving data in a decentralised and secure manner.
Swarm's overlay network is built on top of the underlay transport layer and uses Kademlia overlay routing to enable efficient and scalable communication between nodes. Kademlia is a distributed hash table (DHT) algorithm that allows nodes to locate each other in the network based on their unique identifier or hash.
Swarm's DISC is an implementation of a Kademlia DHT optimized for storage. While the use of DHTs in distributed data storage protocols is common, for many implementations DHTs are used only for indexing file references. Swarm's DISC distinguishes itself from other implementations by instead breaking files into chunks and storing the chunks themselves directly within the DHT.
Each chunk has a fixed size of 4kb and is distributed across the network using the DISC model. Each chunk has a unique address taken from the same namespace as the network node addresses that allows it to be located and retrieved by other nodes in the network.
Swarm's distributed immutable storage provides several benefits, including data redundancy, tamper-proofing, and fault tolerance. Because data is stored across multiple nodes in the network, it can be retrieved even if some nodes fail or go offline.
Built on top of the overlay network is also an incentives layer which guarantees that node operators which share their resources with the network are fairly rewarded for their services.
3. Data Access Layer
The third part of Swarm is a component that provides high-level data access and defines APIs for base-layer features. This layer is responsible for providing an easy-to-use interface for developers to interact with Swarm's underlying storage and communication infrastructure.
Swarm's high-level data access component provides APIs that allow developers to perform various operations on the network, including uploading and downloading data and searching for content. These APIs are designed to be simple and intuitive, making it easy for developers to build decentralised applications on top of Swarm.
4. Application Layer
The fourth part of Swarm is an application layer that defines standards and outlines best practices for more elaborate use cases. This layer is responsible for providing guidance to developers on how to build complex applications on top of Swarm's underlying infrastructure.